Rule Operations
Very much like Signature Operations, reaction rules can be composed as well.
There are several variants for combining rules, each determined by the specific operator employed:
- Composition and nesting
- Tensor product and parallel product
- Merge product
Nesting and parallel product are analogous to composition and tensor product, respectively, but involve name sharing.
caution
Currently, only the parallel product is implemented.
Composing Rules in Parallel
Create Reaction Rules
Three methods are defined that create the signature, and the two rules named A and B. The rules are also displayed below for reference.
import org.bigraphs.framework.core.impl.pure.*;
import org.bigraphs.framework.core.impl.signature.*;
import org.bigraphs.framework.core.reactivesystem.*;
import org.bigraphs.framework.core.exceptions.*;
import static org.bigraphs.framework.core.factory.BigraphFactory.*;
private DynamicSignature sig() {
DynamicSignatureBuilder defaultBuilder = pureSignatureBuilder();
defaultBuilder
.addControl("A", 1)
.addControl("B", 1)
.addControl("C", 1)
.addControl("D", 1)
;
return defaultBuilder.create();
}
private ReactionRule<PureBigraph> createRR_A() throws InvalidReactionRuleException {
DynamicSignature sig = sig();
PureBigraphBuilder<DynamicSignature> bRedex = pureBuilder(sig);
PureBigraphBuilder<DynamicSignature> bReactum = pureBuilder(sig);
bRedex.root()
.child("A").down()
/**/.site().top()
;
bReactum.root()
.child("A").down()
/**/.site()
/**/.child("B")
;
PureBigraph redex = bRedex.create();
PureBigraph reactum = bReactum.create();
ParametricReactionRule<PureBigraph> rr = new ParametricReactionRule<>(redex, reactum);
rr.withLabel("RA");
TrackingMap map = new TrackingMap();
map.put("v0", "v0");
map.put("v1", "");
rr.withTrackingMap(map);
InstantiationMap iMap = InstantiationMap.create(1);
iMap.map(0, 0);
rr.withInstantiationMap(iMap);
return rr;
}
private ReactionRule<PureBigraph> createRR_B() throws InvalidReactionRuleException {
DynamicSignature sig = sig();
PureBigraphBuilder<DynamicSignature> bRedex = pureBuilder(sig);
PureBigraphBuilder<DynamicSignature> bReactum = pureBuilder(sig);
bRedex.root()
.child("C").down()
/**/.child("B").down()
/**//**/.site().child("C")
;
bReactum.root()
.child("C").down()
/**/.child("B").down()
/**//**/.site().child("C")
;
PureBigraph redex = bRedex.create();
PureBigraph reactum = bReactum.create();
ParametricReactionRule<PureBigraph> rr = new ParametricReactionRule<>(redex, reactum);
rr.withLabel("RB");
TrackingMap map = new TrackingMap();
map.put("v0", "v0");
map.put("v1", "v1");
map.put("v2", "v2");
rr.withTrackingMap(map);
InstantiationMap iMap = InstantiationMap.create(1);
iMap.map(0, 0);
rr.withInstantiationMap(iMap);
return rr;
}
note
Both rules have also an instantiation map and a tracking map assigned.
| Rule A | Rule B |
|---|---|
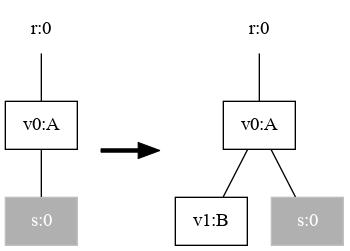 | 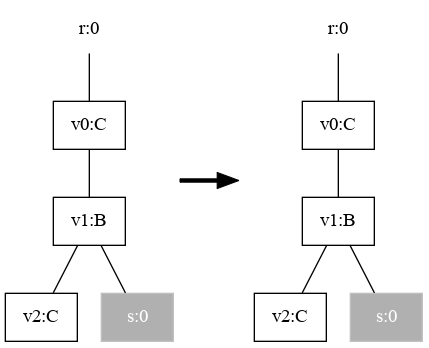 |
Calling the Rule Composer
After having defined the two rules, we can call the ReactionRuleComposer class:
import org.bigraphs.framework.core.*;
import org.bigraphs.framework.core.impl.pure.*;
import org.bigraphs.framework.core.reactivesystem.*;
ReactionRule<PureBigraph> rrA = createRR_A();
ReactionRule<PureBigraph> rrB = createRR_B();
ReactionRuleComposer<ParametricReactionRule<Bigraph<?>>> rComp = new ReactionRuleComposer<>();
ParametricReactionRule<Bigraph<?>> product = rComp.parallelProduct(rrA, rrB);
The result is shown below.
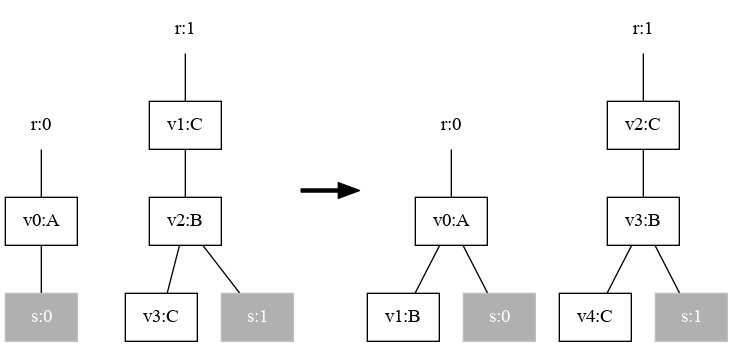
Note that the instantiation map and tracking map has changed as well:
import org.bigraphs.framework.core.reactivesystem.*;
System.out.println("Product label = " + product.getLabel());
assert product.getLabel().equals("RA_PP_RB");
System.out.println(product.getTrackingMap());
product.getInstantationMap().getMappings().forEach((k,v) -> {
System.out.println(k.getValue() + " -> " + v.getValue());
});
Output
Product label = RA_PP_RB
{v0=v0, v1=, v2=v1, v3=v2, v4=v3}
1 -> 1
0 -> 0
tip
The default string separator "_PP_" combines the two rule labels to form a new rule label.
This separator string can be changed by calling ReactionRuleComposer#withSeparator(String).